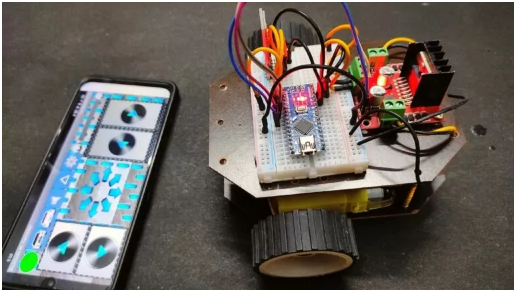
DIY Home Automation Project: How to Make Smart Home with Arduino Uno | Bluetooth Control Tutorial
DIY Smart home: Control Lights and Electronics with Mobile Phone Watch The Tutorial on YouTube Now !! In today’s fast-paced world, the concept of home automation is becoming increasingly popular. Imagine being able to control your home appliances, lights, and security systems with just a tap on your smartphone. Sounds futuristic, right? Well, with the power of Arduino and Bluetooth technology, you can turn this dream into reality. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of DIY home automation and learn how to create a simple yet effective system to control lights using Arduino and Bluetooth. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a hobbyist, or someone looking to add a touch of convenience and innovation to your home, this tutorial is for you. Getting Started: Before we dive into the nitty-gritty details, let’s take a quick look at the components you’ll need for this project: Click on the links below to purchase the components Arduino Uno: The brain of our system, Arduino Uno will be responsible for processing commands and controlling the lights. Programming Cable for Arduino Jumper Wires Relay Module: Used to interface between Arduino and the high-voltage AC circuit of the light bulb. HC-05 Bluetooth Module: Enables wireless communication between Arduino and your smartphone. Light Bulb: Any standard light bulb that operates on 230V AC will work for this project. Light Bulb Holder Two Pin Connector Arduino Starter Kits(For Beginners):- Quad starter kit for Beginners to learn Arduino (Rs 2600-2800) Basic Starter Kit (Rs 1700-1900) Basic Starter Kit (Rs 1200-1400) Setting Up the Hardware The first step is to assemble the hardware components. Connect the relay module to Arduino Uno as per the wiring diagram provided in the Arduino documentation. Ensure that all connections are secure and double-check for any loose wires. Next, connect the light bulb to the relay module. Make sure to follow proper safety precautions when working with high-voltage circuits. Once everything is connected, power up the Arduino Uno using a USB cable or an external power source. Programming Arduino: With the hardware setup complete, it’s time to write the code for Arduino. We’ll use the Arduino IDE to write and upload the code to the board. The code will include instructions for initializing the Bluetooth module, reading commands from the smartphone, and controlling the relay module accordingly. Testing and Troubleshooting: Once the code is uploaded, it’s time to test our home automation system. Download a Bluetooth terminal app on your smartphone and pair it with the HC-05 Bluetooth module. Send commands from the app to Arduino and observe the response of the relay module. Download the Android Application Now Android APP Download NOW!! CODE //search @TheIshanJain on youtube for more // Visit TheIshanJain.Com for More Information Enjoy the code!! String inputs; #define relay1 2 //Connect relay1 to pin 9 #define relay2 3 //Connect relay2 to pin 8 #define relay3 4 //Connect relay3 to pin 7 #define relay4 5 //Connect relay4 to pin 6 #define relay5 6 //Connect relay5 to pin 5 #define relay6 7 //Connect relay6 to pin 4 #define relay7 8 //Connect relay7 to pin 3 #define relay8 9 //Connect relay8 to pin 2 void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); pinMode(relay1, OUTPUT); pinMode(relay2, OUTPUT); pinMode(relay3, OUTPUT); pinMode(relay4, OUTPUT); pinMode(relay5, OUTPUT); pinMode(relay6, OUTPUT); pinMode(relay7, OUTPUT); pinMode(relay8, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(relay1, LOW); digitalWrite(relay2, LOW); digitalWrite(relay3, LOW); digitalWrite(relay4, LOW); digitalWrite(relay5, LOW); digitalWrite(relay6, LOW); digitalWrite(relay7, LOW); digitalWrite(relay8, LOW); } void loop() { while(Serial.available()) { delay(10); char c = Serial.read(); if (c == ‘#’){ break; } inputs += c; } if (inputs.length() >0) { Serial.println(inputs); if(inputs == “A”) { digitalWrite(relay1, LOW); } else if(inputs == “a”) { digitalWrite(relay1, HIGH); } else if(inputs == “B”) { digitalWrite(relay2, LOW); } else if(inputs == “b”) { digitalWrite(relay2, HIGH); } else if(inputs == “C”) { digitalWrite(relay3, LOW); } else if(inputs == “c”) { digitalWrite(relay3, HIGH); } else if(inputs == “D”) { digitalWrite(relay4, LOW); } else if(inputs == “d”) { digitalWrite(relay4, HIGH); } else if(inputs == “E”) { digitalWrite(relay5, LOW); } else if(inputs == “e”) { digitalWrite(relay5, HIGH); } else if(inputs == “F”) { digitalWrite(relay6, LOW); } else if(inputs == “f”) { digitalWrite(relay6, HIGH); } else if(inputs == “G”) { digitalWrite(relay7, LOW); } else if(inputs == “g”) { digitalWrite(relay7, HIGH); } else if(inputs == “H”) { digitalWrite(relay8, LOW); } else if(inputs == “h”) { digitalWrite(relay8, HIGH); } inputs=””; } }